The aim of this new line of business, named CADE COBOTS, is to develop, supply and integrate complete “turnkey” solutions for the automation and optimization of industrial processes, through collaborative robots.
The changes towards an intelligent industrial model, which can be adapted to specific needs and processes , are the fundamental concepts of a revolution that has already started as an unstoppable reality and its name (INDUSTRY 4.0) is in fact known and used by a good part of our society.
The concept of industry 4.0 is supported by several technological foundations, with different degrees ofmaturity and capacity for immediate implementation in the industry (Additive Manufacturing, Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), Cyber-physical Systems, Big Data, Virtual Reality (VR), or Artificial Intelligence (AI), among others).
Among all the technological basis that sustain this concept in the industrial manufacturing field, collaborative robotics is standing out, both in terms of technological maturity and capability to generate changes.
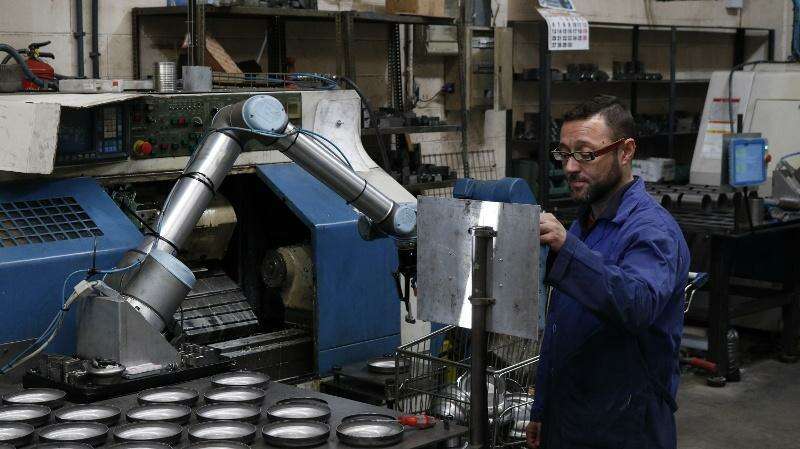
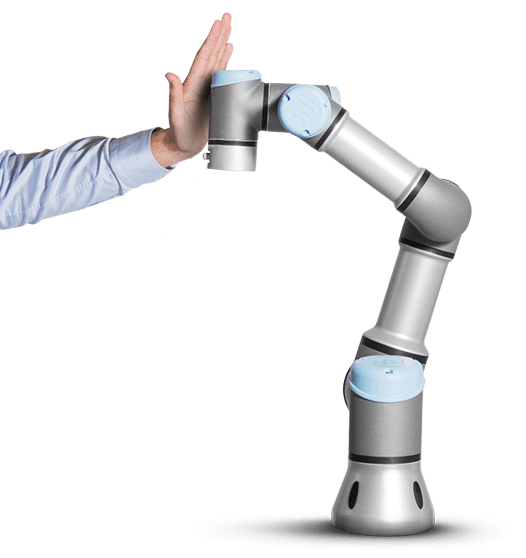

Using cobots allows to optimize de productivity and redirect the operator’s responsibilities towards other processes, with a higher specialization and value. They are mainly used to reduce the workload in monotonous and repetitive tasks with little or no value, tasks whose productivity depends exclusively on the operator and which may also carry physical or mental health risks.
Cobots can be easily reconfigured to be used for a different process or relocated in a different point of the production line. Therefore, the productive capacity of an industry becomes more flexible, regardless of its activity or size.
Plug & Play Robotics
| Fixed installation taking space. High safety requirements. |
| Human interaction not allowed. |
| Singles tasks or processes assigned. |
| Expensive programming that can only depend on its administrator. |
| High investment, return in several years. |
| Different facilities. No additional space required. |
| With frequent interaction |
| Developing multiple tasks |
| Easily and quickly programming, that can be done by any operator |
| Return on investment in less than a year |
1. They are safe: they do not need fences or protected and set aside spaces, they do not require large spaces for their installation either.
2. They are collaborative: they can work hand in hand with people. A single operator can work with several cobots.
3. They are flexible: They can perform almost any handling task or operation, being also easily to transport and configure to be relocated in different positions.
4. They are easy to program: Any operator without a previous qualification can learn in a few minutes how to use a cobot and how to reprogram it for a new task.
5. They are economic: Compared to traditional industrial robots, whose return on investment takes several years, the return on investment of a cobot usually takes less than a year. The investment required is substantially lower, which makes it accessible to the SME.

‘The only thing all industries have in common is that they all are different’






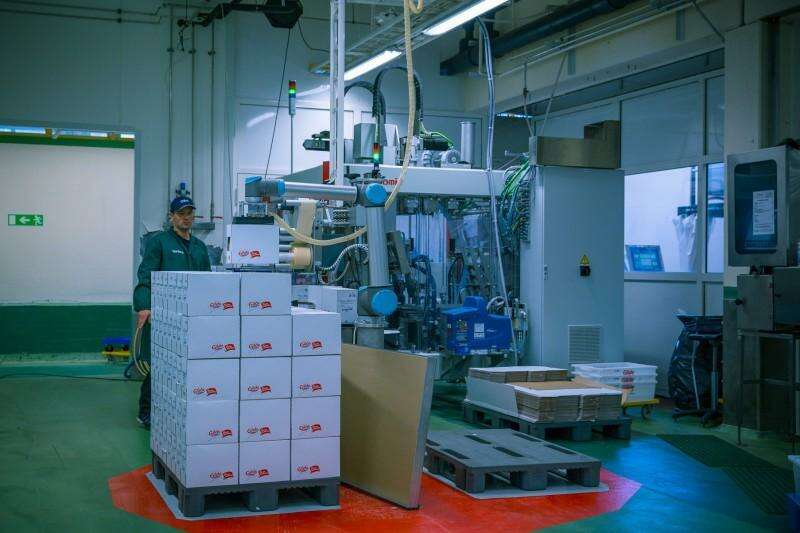
The industrial sectors that are already incorporating COBOTS in their productive processes are innumerable and it is expected that many others will immediately join this unstoppable trend.







Pilot project: CADE COBOTS DEMO
In order to show the extraordinary integration capacity of this new generation of robots and its applicability in small and medium enterprises, CADE COBOTS launched a demonstration project in July 2018 in a metal fabrication workshop.
The project consisted of using a COBOT (UR10 model) to automate the process of placing metal parts and removing the final assembly after a welding process carried out by an existing industrial welding robot. This process was being steadily performed by one of workers.
The project’s objective was to develop a real experience of a cobot implementation in a workshop at full workload and with a specific order for a final customer.
Apart from the integration of the collaborative process with the existing welding robot, it was particularly important to see how the implementation of the COBOT did not affect the normal activity of the workshop, unlike the traumatic integrations associated to automation systems with traditional robotics.
After two weeks of operation and with 3500 finished pieces, the owner of the workshop asserted that the production ratios obtained with the cobot were well above those obtained through traditional manual processes. In addition, the same worker that was previously in charge of the assembly operation, was now able to carry out, among other tasks, the inspection and supervision of finished parts, a task that used to be executed as an additional process.
The solution implemented by CADE consisted of an automated feeding system including supply, installation and configuration of the own cobot, as well as the system of feeding and automated removal of parts, integrating this process with the existing welding robot.
During the demonstration project, companies from different sectors and activities visited the facility and shared their own point of view about the applicability of collaborative robotics in their own processes, having a positive general response.
As a result of this round of visits, specific studies will be carried out for different processes, including detailed studies of the current process and technical and economical evaluation of solutions based on cobots.
Derivados de esta ronda de visitas se realizarán estudios particulares para distintos procesos incluyendo estudios pormenorizados del proceso actual y evaluación técnica y económica de soluciones basada en cobots.












