Tags: Pressure Vessels, Piping, Integrity Engineering
Corrosion under insulation (CUI) is defined as a type of corrosion (general corrosion or localised corrosion) caused by trapped water on surfaces covered with insulation. Another type of corrosion similar to CUI is corrosion under fireproofing (CUF), both classified within the same damage mechanism.
Content
When insulation is required?
Usually, insulation is required in pressure vessels and pipes in the following situations:
- Heat conservation (usually for pressure vessels/ pipes whose operation temperatures are higher than 100ºC).
- Cold conservation (for example, cryogenic pipe systems).
- Personal protection insulation, usually when surface temperatures of pressure vessel or pipes exceed 60ºC. Personal protection insulation is required to avoid any personal damage in contact with these surfaces.
- Fire protection.
- Noise reduction.
CUI - Chemical Reaction
The chemical reaction of CUI requires at least the following elements:
- Anode.
- Cathode.
- Electrolyte.
- Oxygen (air)
Following electrochemical reaction occurs typically during CUI:
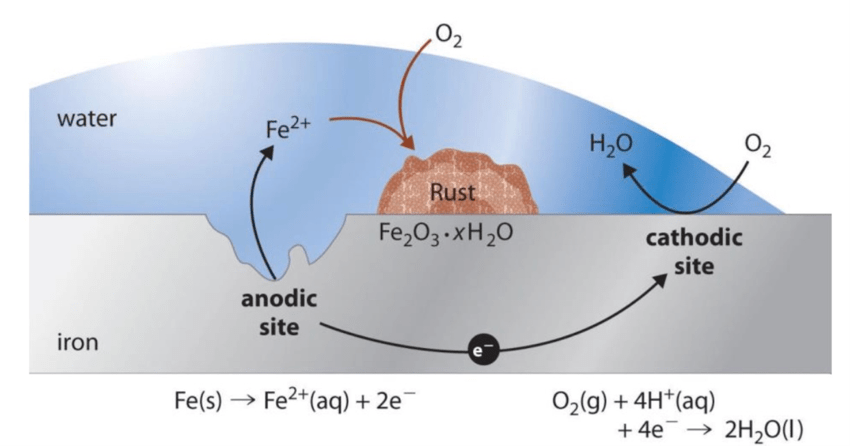
Locations on pressure vessels susceptible to CUI Damage
Following areas of pressure vessels are susceptible to have corrosion under insulation (CUI):
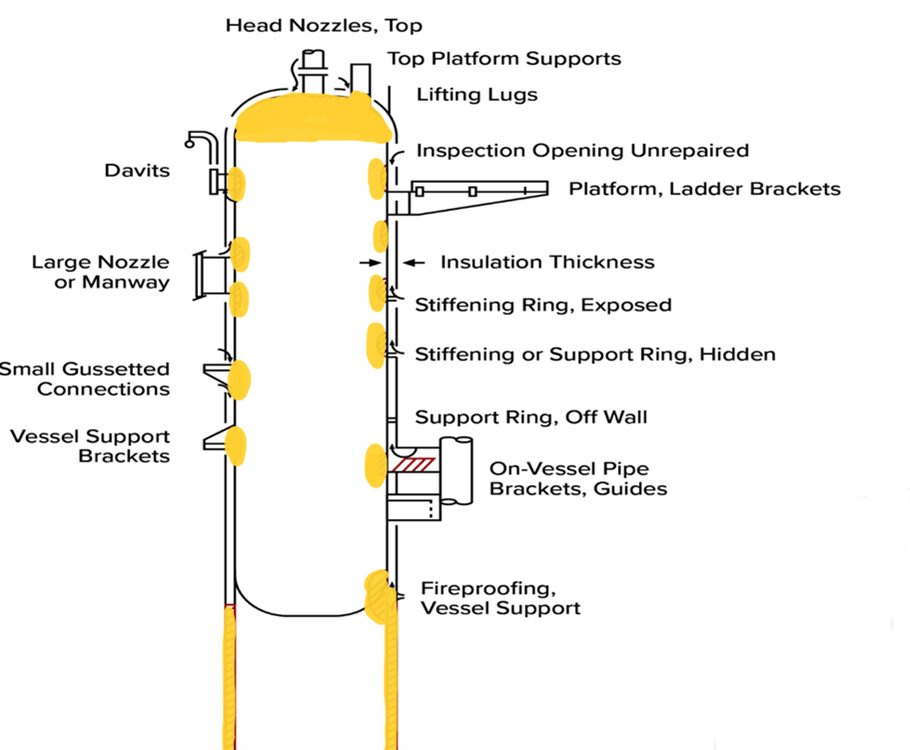
Usually, zones to be susceptible to have corrosion under insulation (CUI) are zones where insulation is not correctly installed or maintained during the normal operation of pressure vessel or piping components.
The following picture shows a susceptible area in a piping system (in this case located on piping support).
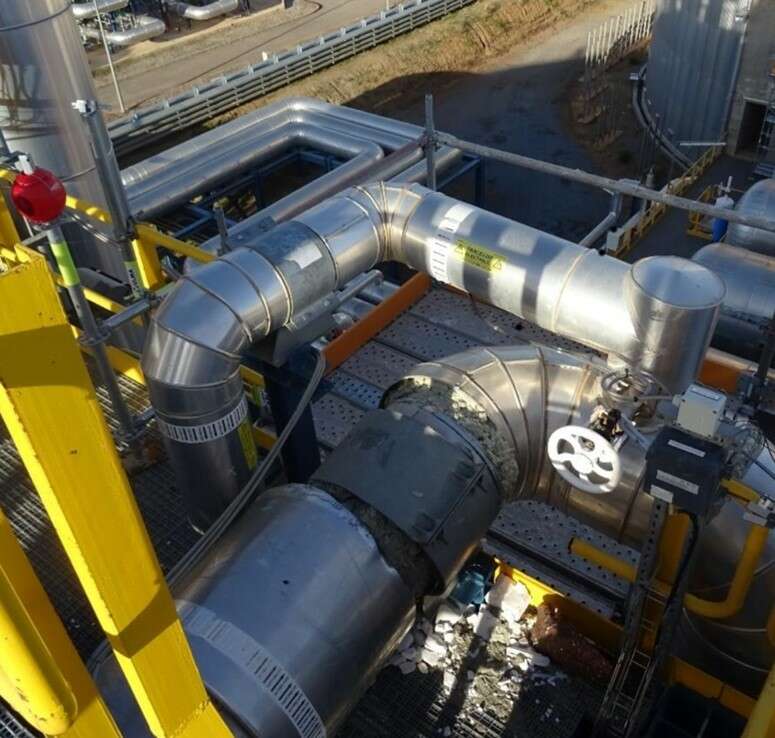

Could corrosion under insultation (CUI) be prevented?
In general, corrosion under insulation (CUI) could be mitigated if water ingressed into the insulation system is eliminated and if the metal surface of the piping or pressure vessel component is maintained dry during different stages of the installation and operating life.
MANUFACTURING AND INSTALLATION
An exhaustive control and supervision during initial manufacturing and installation can prevent defects on insulation, therefore, risks of CUI will be reduced.
REPARATION, MAINTENANCE DURING OPERATION
A correct replacement or maintenance of insulation during different reparations and upgrades on piping and pressure vessels can also reduce the risk of CUI
INSPECTION PLAN
The most important preventive action that can reduce the risk of CUI on elements is having a good plan of inspection and control of zones which are susceptible to corrosion under insulation (CUI). Visual inspection, radiography (x-ray) (RX) inspection, ultrasonic testing (UT), and liquid penetrant surface examination (PT) are the most common methods to control corrosion mechanisms.

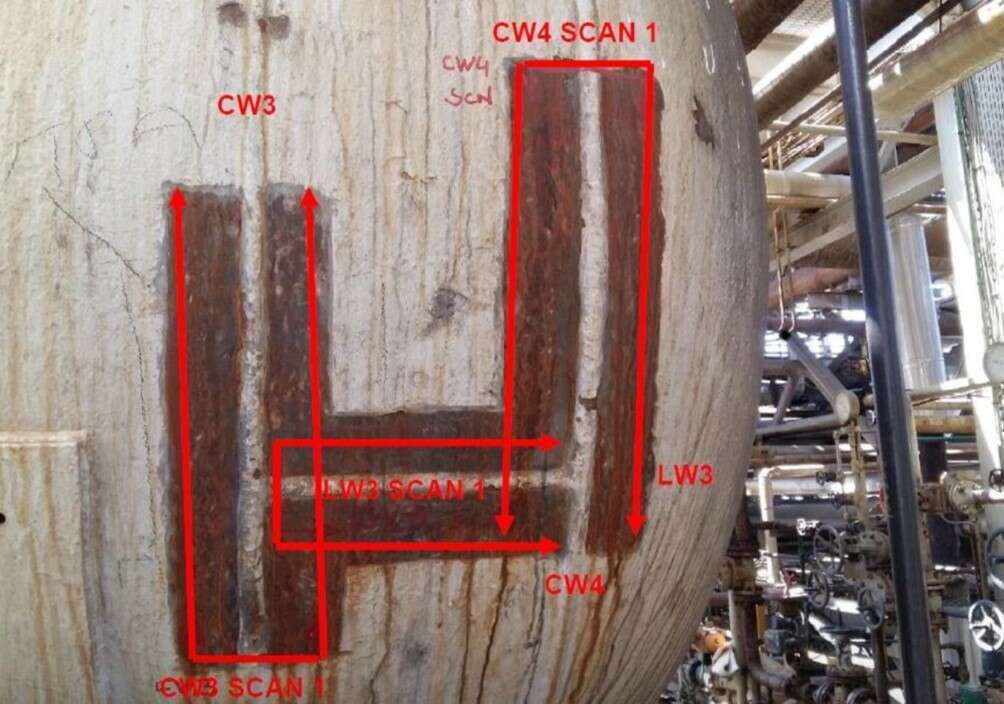
CUI damage detected: How to proceed?
When a CUI damage is detected following actions or steps shall be followed:
- Identify the type of damage (local corrosion or general corrosion).
- Perform FFS Assessment according to API-579 / ASME FFS – Part 4 (Level 1, Level 2 & Level 3) in case of general corrosion damage is detected.
- Perform FFS Assessment according to API-579 / ASME FFS – Part 5 (Level 1, Level 2 & Level 3) in case of general local damage is detected.
- Repair or replacement of the damaged component. It must be taken into consideration that this is the most undesirable case due to the high cost of unplanned stops on industries.

CADE's experience on FFS calculations
CADE engineering is the best partner for the performance of FFS evaluations (from FFS Level 1 to FFS Level 3 by finite element analysis), as we count on a extensive engineering knowledge and expertise (with more than 1800 projects in more than 15 years of activity), highly skilled and committed team of engineers, alongside a solid business management, which make CADE an independent leading engineering and consultancy company around technology, equipment and plants within Oil & Power industries among other industries.
Further information
For any query or request for additional information about our services and technologies, please complete the following form:













