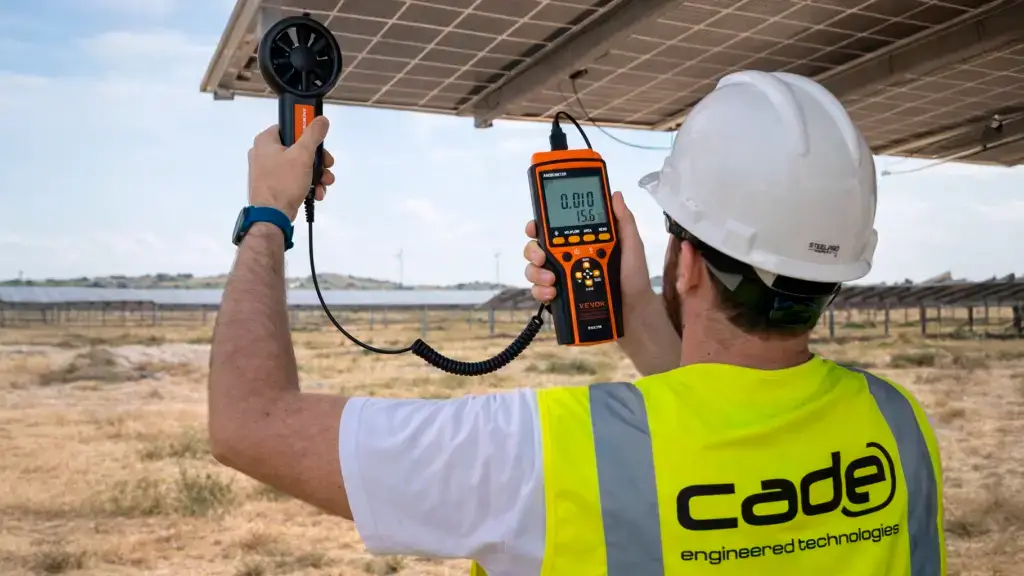
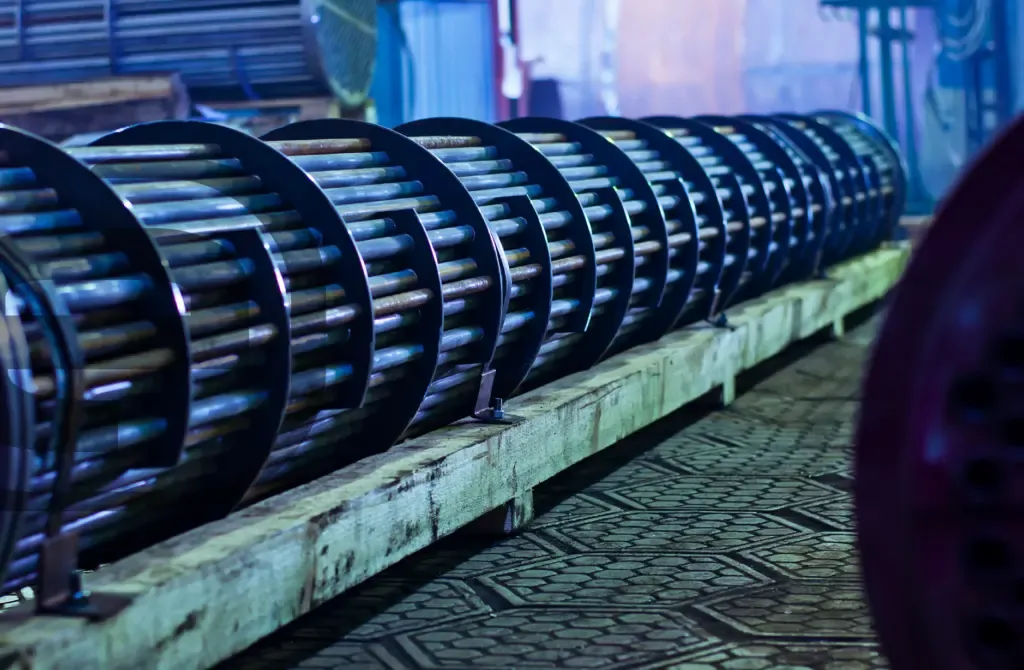
During the life cycle of many pressure vessels arise the necessity to maintain them in service after detecting crack-like flaws or delamination. For that, there are some methodologies that allow establishing a quantitative judgment about if it is possible to safely operate this equipment and also determine its remaining life until it must be repaired or substituted. This type of study allows plant owners to save costs because it permits the pressure vessels to operate safely after detecting the presence of faults. 
In order to keep in service pressure vessels which present crack-like flaws, CADE is able to establish a quantitative engineering judgment based on the methodologies provided in Part 9 of API-579/ASME FFS-1.
There is a big casuistic of crack-like flaws (internal or external, parallel or perpendicular to the thickness, coalescence of microcracks, close to a weld…). To analyze that, Part 9 of API-579/ASME FFS-1 provides some analysis levels that allow determining the aptitude for service:
- Level 1 and Level 2 assessments are based on the fracture mechanics theory and evaluate the crack-like flaws using the Fracture Assessment Diagram (FAD). Both procedures allow to quickly establish a quantitative judgment. But in some cases, these procedures are overly conservative, or they cannot be applied because of the code limitations.
- Level 3 assessment requires advanced techniques based on simulation by means of a Finite Element Method analysis (FEM) to determine the stress fields and the energy released by the crack (JIntegral). Although this assessment is the most complex, it allows us to analyze a big casuistic of crack-like flaws.
Although the level 3 assessment is more complex than the level 1 & 2, it provides less conservative results and allows the analysis of a greater casuistic of cracks. The level 3 analysis is particularly recommended in the following cases:
- Cracks that do not meet the requirements for the “Level 1 and 2 assessments”.
- Cracks located in complex geometries.
- Cracks located close to welds in the heat-affected zone (HAZ)
- Cracks located in zones with high-stress levels.
- Crack-like flaws that could continue growing in service.
CADE counts on a significant track record on integrity assessments and remaining life procedures for pressure vessels. Also, CADE has experience in the evaluation of the operational data and the definitions of the inspection and maintenance procedures.
Further information
For any query or request for additional information about our services and technologies, please complete the following form:












