Post weld heat treatment (PWHT) is a thermal treatment usually performed in steels that have been welded. Its object is to ensure that the welding properties are suitable for its expected operation according to the mechanical and structural requirements prescribed in the corresponding design codes. This kind of treatment is usually performed on pressure equipment and pipes within refineries, petrochemical and power plants.
Depending on used material and thickness of the welded parts, PWHT might become a mandatory requirement, according to the design codes commonly used for pressure equipment and piping design (ASME VIII, B31.3, EN -13445, AD-2000, etc.).
By means of a proper PWHT, temperature is raised around welded area in order to eliminate residual stresses generated during the welding process (stress relief) and thus reducing the hardness of the heat-affected zone (HAZ).
In case of application of a non-adequate PWHT, residual stress or excessive hardness may appear in the joint area after welding. This phenomenon, in combination with the stresses caused by the regular equipment operation (pressure, temperature, etc.) might lead to a mechanical instability or generate, in the worst case scenario, plastic collapse failures, fatigue damage or stress corrosion cracking phenomena.
PWHT parameters (temperature and time) to be applied will be defined by internal fluid, material and thickness, as well as by the requirements of design code or owner/licensor’s specifications.


Along manufacturing stage, PWHT treatment is usually carried out at the workshop facilities with specialized furnaces aimed for such process. Depending on furnace’s capacity, thermal treatment can be performed for the one-piece equipment. This way, significant thermal gradients are avoided and thus the appearance of residual stress and excessive hardness in the joint zone are considerably minimized. In general terms, when the PWHT is conducted along manufacturing stage, a detailed evaluation of its impact on equipment’s mechanical behavior does not result strictly mandatory.
Along plant scheduled turnarounds or shutdowns due to repairs or modifications, welding operations and the subsequent PWHT must be performed on-site. Such interventions will be generally localized on specific zones of the equipment thus Local PWHT might generate significant thermal gradients between the treated areas and the rest of the areas not be affected by the thermal treatment.
These thermal gradients can lead to mechanical instability issues (residual stress, excessive joint hardness, stress corrosion cracking, etc.). In most cases, these defects are not straight detected, which could result in future mechanical issues throughout the equipment’s service life. (e.g. Stress corrosion cracking).
Failures or breaks in operating equipment, which may lead to a unit shutdown, imply a serious tricky issue that could be prevented and even avoided, with the corresponding control and analysis of local post-weld heat treatments.

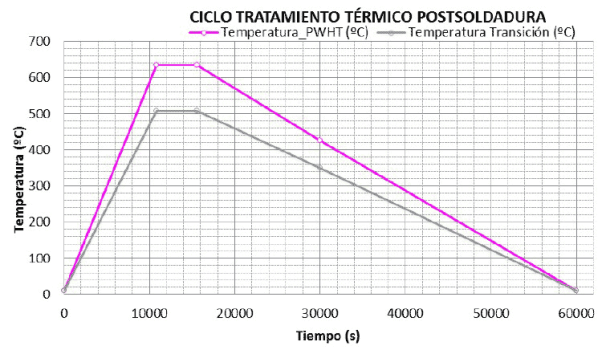
Therefore, and in case of heat treatments on-site, definition and validation of the right parameters of PWHT result highly recommendable in terms of mechanical integrity compliance and code requirements.
From a technical point of view, such evaluations are usually approached through a transient analysis using the finite element method, which considers treatment temperatures, geometries to be treated and transition temperatures, based on the guidelines and recommendations of WRC-452 “Recommended practices for local heating of welds in pressure vessels”, and ASME VIII Division 1 UCS-56 design code.
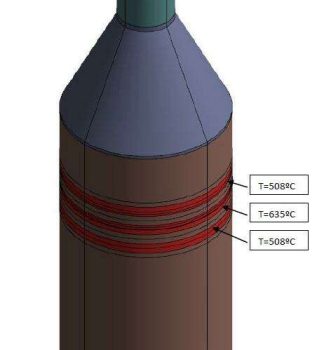
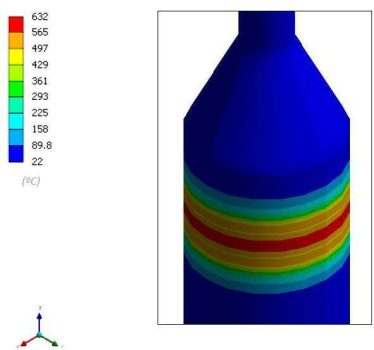
In and out temperatures during transient analysis with finite element.
Results validation is conducted according to design code ASME VIII Division 2, Part 5 “Design by analysis requirements” / API 579-1 ASME FFS-1 “Fitness for service, evaluation of protection against local failure in elastic-plastic range”, so that residual stress and permanent plastic deformations (if any) should be below the limits established by these codes.
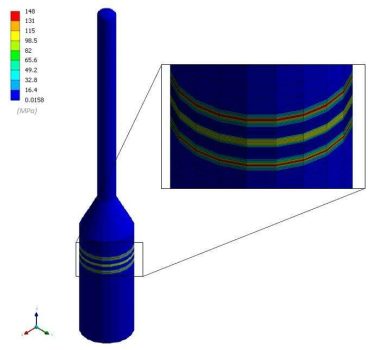
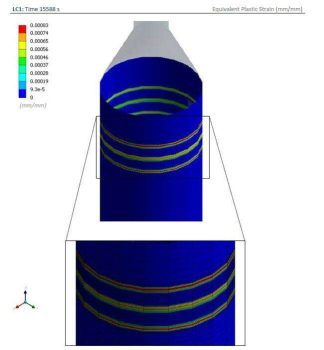
Finally, a buckling analysis is performed to ensure the equipment or vessel stability during the Post Weld Heat Treatment (PWHT) for wind/seismic loads.
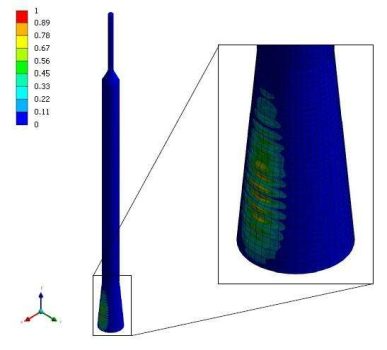
- Conclusions derived from the analysis will allow to validate the mechanical integrity of the equipment during and after the PHWT treatment. Moreover, these conclusions will determine and validate the parameters of the thermal treatment to be applied: both heating and cooling ramps and treatment times. The analysis will also help to reduce the instability risks of the equipment against wind / seism loads during the process.
- Likewise, the analysis will allow to define in advance the required means for the right performance of the Post Weld Heat Treatment (heating blankets, electricity generators, auxiliary machinery, etc.), in order to ease appropriate resources and time planning.
- It is usual practice to evaluate circumferential welding of vertical equipment, welding of skirts or welding of support cradles, among other examples.
CADE has a wide experience as an engineering and consulting company specialized in design of pressure equipment and evaluation of mechanical integrity in critical operating equipment. CADE provides comprehensive engineering and consulting services to plant owners, EPC contractors, and equipment suppliers: thermal, hydraulic, process and mechanical design, preparation of design specifications and technical requirements, procurement, owner’s engineering, performance evaluation, integrity assessment consultancy or expert witness services, among other capabilities.
Albacete
Parque Científico y Tecnológico
Paseo de la Innovación 3, 02006 Albacete – España
Tel. +34 967 19 01 72
C/Raimundo Fernández Villaverde, 53 (Entreplanta)
28020
Madrid – España
Albacete
Parque Científico y Tecnológico
Paseo de la Innovación 3, 02006 Albacete – España
Tel. +34 967 19 01 72
C/Raimundo Fernández Villaverde, 53 (Entreplanta)
28020
Madrid – España
If you please, contact us and tell us about your project to inform you what we can do for you
We inform you about our engineering solutions