ATJ EPC Project
Automation System for Santiago Bernabéu Stadium.
Owner’s Engineering and PMS
📍Madrid (Spain)
Description
Project
In 2019, Real Madrid C.F. launched the ambitious remodelling of the Santiago Bernabéu Stadium, aiming to position it as a global benchmark in sports and entertainment venues.
Among the main objectives of this transformation was the creation of new revenue streams through an innovative operational model that would enable the stadium to be used 365 days a year.
One of the core elements of this transformation is the automated retractable pitch system, stored underground and equipped with state-of-the-art technologies for the maintenance and preservation of the turf in optimal conditions.
The executive design was developed by SENER, while the EPC (Engineering, Procurement and Construction) contract was awarded to PHB Weserhütte in 2021.
From the early stages, CADE acted as technical advisor to Real Madrid C.F., supervising the executive design and the EPC tendering process. Subsequently, CADE took on PMT (Project Management Team) and Owner’s Engineering roles, ensuring optimal project performance from technical, economic, and scheduling perspectives.
Videos Real Madrid C.F
25-meter-long trusses assembled inside the stadium
Meters deep, for storing pitch trays
Tons of structural steel
Background
ATJ Project
he execution of the ATJ System (Automated Turf System) began in May 2022, following the last UEFA Champions League match held at the Santiago Bernabéu Stadium. The first activities included dismantling the existing pitch, with the immediate goal of having the new system ready for the first league match on September 3, 2022.
The ATJ system is composed of six mobile trays, each measuring 107 x 11.6 meters and weighing approximately 1,500 tons. These trays rest on an underground hypogeum located nearly 30 meters below the field surface. The technical infrastructure includes metallic structures and mechanical equipment totaling more than 5,000 tons. The system also integrates 22 redundant hydraulic mechanisms to ensure high-precision tray movement.
Additionally, the system comprises approximately 90 kilometers of electrical cabling and more than 5 kilometers of piping, distributed between the agronomic maintenance facilities and fire protection systems. For its development and documentation, over 12,500 technical documents were produced—nearly 11,500 of which were drawings.
This large-scale project involved:
40 engineering, consulting, and surveying firms
16 logistics companies
66 industrial supply and raw material providers
40 manufacturing companies
30 assembly contractors
Execution required over 350,000 direct assembly hours and the use of more than 1,250 trucks for material transportation, including those used to remove the pitch at the end of the 2021/22 season.
In November 2023, the ATJ system achieved Provisional Acceptance, following CADE’s supervision and validation of its operational and maintenance performance. Real Madrid C.F. President Florentino Pérez highlighted this milestone as a major success during the club’s General Assembly.
Mechanisms Associated
with the ATJ System
Lifting System
Translation Carts
Storage
Growth Lighting
Radiant Floor Heating
Irrigation
Otros Proyectos

Fatigue Analysis Of Process Equipment Using Finite Element Method
FATIGUE ANALYSIS OF PROCESS EQUIPMENT USING FINITE ELEMENT METHOD OBJECTIVE A significant supplier of process equipment and pressure vessels requested CADE’s services to perform design validation for fatigue of a

Structural Analysis of Railway Rolling Stock Incorporating Suspension System
Structural Analysis of Railway Rolling Stock Incorporating Suspension System Advantages of incorporating the suspension system to finite element analysis CADE normally uses the Finite Element Method (FEM) to undertake simulation
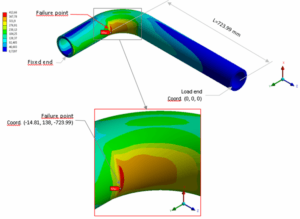
Stress Intensity Factor (SIF) For Special Geometries in Piping Stress Analyisis
Stress Intensity Factor (SIF) For Special Geometries in Piping Stress Analyisis SIF according to ASME B31J for special geometries not covered in ASME B31.1 and ASME B31.3 codes PROBLEM DEFINITION
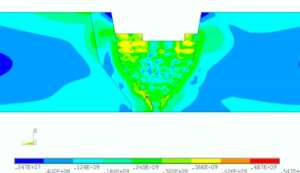
ROOT CAUSE ANALYSIS AND CORRECTIVE MEASURES OF DISSIMILAR WELD JOINT FAILURE IN A HIGH PRESSURE STEAM PIPE
Root Cause Analysis And Corrective Measures Of Dissimilar Weld Joint Failure In A High Pressure Steam Pipe PROBLEM DEFINITION During the operation of a petrochemical plant (located in Middle East),

